A) 7,550.
B) 8,000.
C) 8,400.
D) 8,800.
E) 9,250.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Structural unemployment refers to unemployment resulting from:
A) technological change.
B) being in the wrong geographical location
C) taking the time to find the best job.
D) seasonal decreases in demand for labor.
E) a recession in the economy.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of frictional unemployment is a(n) :
A) textile worker permanently laid off due to jobs lost to imports.
B) engineer permanently laid off due to advances in technology.
C) fast-food restaurant worker who quits work and attends college.
D) computer programmer who leaves one job and accepts a new job.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Louise is unemployed due to a decrease in the demand for workers with a knowledge of a certain word processing language. This is an example of:
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) involuntary unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The four phases of a single business cycle are, in order, the trough, followed by a recovery, then a recession, ending with a peak.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 6-2 Unemployment categories 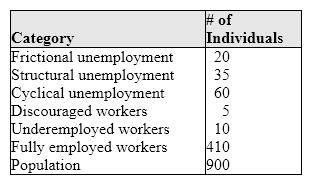 Find the BLS's rate of unemployment from the following data: frictional unemployment = 150, structural unemployment = 200, cyclical unemployment = 225, discouraged workers = 25, underemployed workers = 75, fully employed workers = 850, total population = 2,000.
Find the BLS's rate of unemployment from the following data: frictional unemployment = 150, structural unemployment = 200, cyclical unemployment = 225, discouraged workers = 25, underemployed workers = 75, fully employed workers = 850, total population = 2,000.
A) 17.5 percent
B) 23.3 percent
C) 24.6 percent
D) 28.8 percent
E) 38.3 percent
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Recovery is the phase of the business cycle during which real GDP reaches its maximum.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The number of people officially unemployed is not the same as the number of people who can't find a job because:
A) the armed forces is included.
B) some people have jobs but continue to look for a better one.
C) some people who can't find a job become discouraged and quit looking.
D) none of these.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is difficult for cyclically unemployed individuals to find jobs because:
A) they do not meet the qualifications required for the available jobs.
B) the economy is in a recession.
C) they quit their last job and employers view them with suspicion.
D) they have not looked long enough to find a job.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following offers an example of frictional unemployment?
A) The rise in unemployment for stable workers after the development of gasoline-powered automobiles and the resulting long-tern decline in horse-and-buggy transportation.
B) The rise in unemployment among farm workers after harvest.
C) Unemployment resulting from the business cycle.
D) None of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
John Steinbeck's Cannery Row describes a character who takes his own life because of poor job prospects. If he was an unemployed person who gave up looking for work, he would be considered:
A) chronically unemployed.
B) a discouraged worker.
C) a member of the labor force.
D) frictionally unemployed.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of structural unemployment is a(n) :
A) textile worker who quits one job and waits for the new job to begin.
B) engineer permanently laid off due to advances in technology.
C) computer programmer who becomes rich and leaves the labor force.
D) All of these.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A general rule is that economy is experiencing a recession when:
A) real GDP declines for at least three months.
B) real GDP declines for at least nine months.
C) nominal GDP declines for at least nine months.
D) real GDP declines for at least six months.
E) nominal GDP declines for at least six months.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The GDP gap is the difference between:
A) frictional unemployment and actual real GDP.
B) unemployment rate and real GDP deflator.
C) actual real GDP and full-employment real GDP .
D) full-employment real GDP and real GDP deflator.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true ?
A) The four phases of the business cycle, in order, are: peak, recovery, trough, recession.
B) When unemployment is rising then real GDP is rising.
C) The economic problem typically associated with a recovery is rising unemployment.
D) Full employment exists in an economy when the unemployment rate equals the sum of frictional, and structural unemployment rates.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in aggregate demand and the subsequent cutbacks in production lead to:
A) frictional unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) cost-push unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
E) transitory unemployment.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The civilian labor force consists of:
A) all civilians over the age of 16.
B) the employed plus the unemployed who are not in the military.
C) only individuals who are actually at work during a given week.
D) civilians who are not in prisons or mental hospitals.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sam is a musician who is out of work because electronic equipment replaced live musicians. This is an example of:
A) frictional unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) involuntary unemployment.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider an economy made up of 100 people, 60 of whom old jobs, 10 of whom are looking for work, and 15 of whom are retired. The number counted as unemployed is:
A) 10.
B) 15.
C) 40.
D) 30.
E) 90.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following groups of people are counted as employed?
A) People who work at least one hour a week.
B) People who work at least 15 hours a week as unpaid employees of a family business.
C) People who are out of work due to bad weather.
D) All of these are counted as employed.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 194
Related Exams